Get information related to Explain Why Dna Replication Is Considered To Be Semi-Conservative that you’re searching for in this article, hopefully it can assist you.
The essence of life lies within the intricate double helix of DNA, the blueprint that orchestrates the functions and characteristics of every living organism. At the heart of DNA’s remarkable abilities is its capacity for replication, the process by which it meticulously duplicates itself to ensure the faithful transmission of genetic information. One of the fundamental principles governing DNA replication is its semi-conservative nature, a concept that has profound implications for our understanding of heredity.
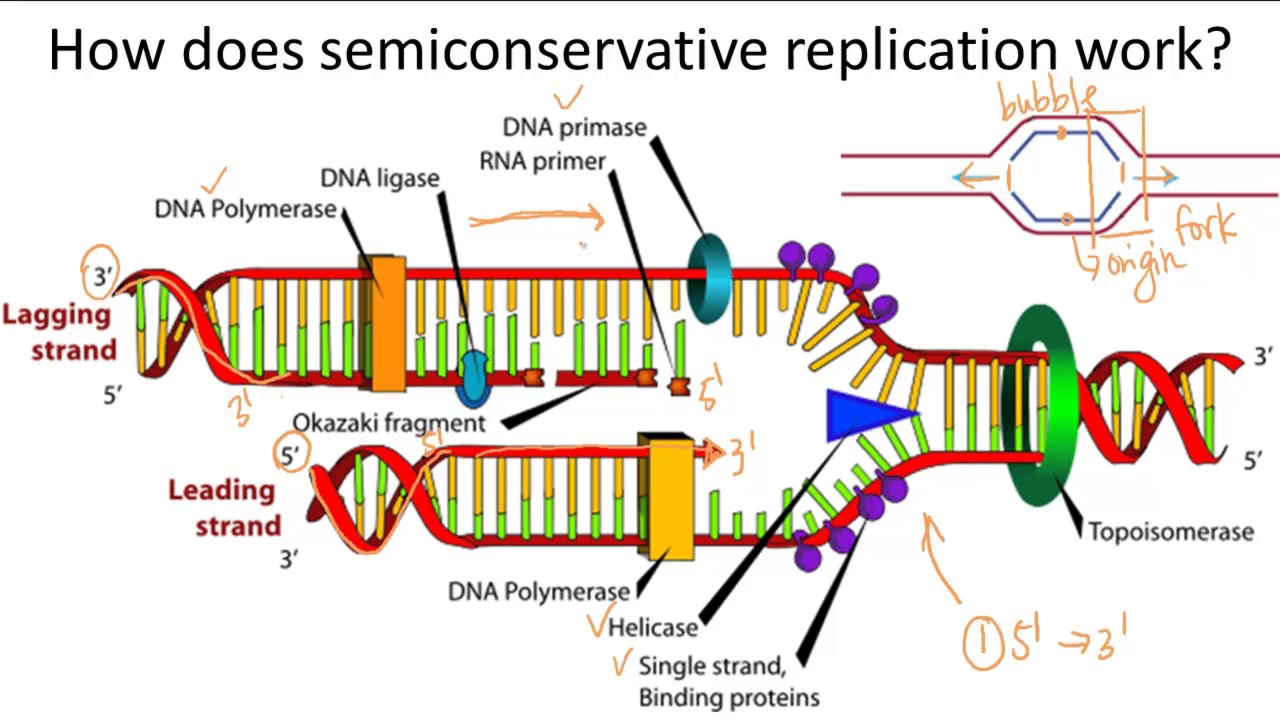
Explain Why Dna Replication Is Considered To Be Semi-Conservative
Before delving into the intricacies of DNA replication, let’s pause to appreciate the magnitude of this intricate biological process. Every time a cell divides, it must precisely duplicate its entire genome, consisting of billions of base pairs. The accuracy of this replication is paramount, as even a single error can have devastating consequences for the cell and the organism it inhabits.
Semi-Conservative Replication: Unveiling the Process
The term “semi-conservative” refers to the fact that each newly synthesized DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This concept was first proposed by scientists Watson and Crick in 1953, based on their groundbreaking work on the structure of DNA. Subsequent experiments by Meselson and Stahl in 1958 provided irrefutable evidence to support the semi-conservative model.
During DNA replication, the DNA double helix unwinds, allowing each strand to serve as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This process is carried out by a molecular machine called DNA polymerase, which adds complementary nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine) to the growing DNA chain, following the base-pairing rules (A with T, C with G). As a result, each daughter DNA molecule inherits one original strand and one newly synthesized strand, hence the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication.
Significance of Semi-Conservative Replication
The semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication has profound implications for our understanding of genetics and heredity. It ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic information, maintaining the integrity of the genome throughout generations. Moreover, it provides a mechanism for DNA repair, allowing cells to correct errors that may arise during replication.
In addition, the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication explains the phenomenon of genetic mutations. Mutations occur when changes are introduced into the DNA sequence during replication, leading to the production of non-identical daughter DNA molecules. These mutations can be beneficial, harmful, or neutral, and they serve as the driving force behind genetic variation and evolution.
Current Trends and Developments
In recent years, advances in DNA sequencing technologies have enabled researchers to study DNA replication in unprecedented detail. These studies have revealed the remarkable fidelity of DNA polymerase and the intricate mechanisms that ensure accurate replication. Additionally, research has focused on understanding the role of epigenetics in DNA replication, exploring how environmental factors can influence DNA methylation and other modifications that affect gene expression.
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of DNA replication, shedding light on its fundamental importance in biology and its implications for human health. By delving deeper into this intricate process, we gain a profound appreciation for the remarkable intricacies of life’s blueprint and its role in shaping our world.
Tips and Expert Advice
For those interested in exploring the topic of DNA replication further, consider the following expert advice:
- Enroll in a biology or molecular biology course that covers DNA replication in depth.
- Read scientific articles and textbooks on DNA replication, such as those published in reputable journals like Nature and Cell.
- Attend conferences and workshops on DNA replication to learn from experts in the field.
- Join online forums and discussion groups dedicated to DNA replication to engage with others and stay updated on the latest research.
- Consider pursuing a career in research or academia to contribute to the ongoing exploration of DNA replication and its implications.
These recommendations provide a pathway to acquire comprehensive knowledge and expertise in the fascinating field of DNA replication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why is DNA replication considered semi-conservative?
A: DNA replication is semi-conservative because each daughter DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Q: How does the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication ensure genetic continuity?
A: The semi-conservative nature of DNA replication ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic information, maintaining the integrity of the genome.
Q: Can DNA replication occur without errors?
A: While DNA replication is highly accurate, errors can occur infrequently due to factors such as environmental stress or mutations in DNA polymerase.
Q: What is the significance of DNA methylation in DNA replication?
A: DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification that can influence gene expression. It can be inherited and can affect the rate and fidelity of DNA replication.
Q: How have advances in DNA sequencing technologies impacted the study of DNA replication?
A: Advances in DNA sequencing technologies have allowed researchers to study DNA replication in unprecedented detail, providing insights into the fidelity and mechanisms of replication.
Conclusion
DNA replication, the process by which DNA duplicates itself, lies at the heart of life’s continuity. Its semi-conservative nature ensures that genetic information is accurately transmitted from one generation to the next, preserving the stability and integrity of the genome. This intricate process has profound implications for heredity, evolution, and our understanding of life itself. Whether you are a curious student, a budding scientist, or simply fascinated by the intricacies of life, the topic of DNA replication offers a captivating journey into the fundamental principles that govern the living world.
Are you intrigued by the complexities of DNA replication and its implications for life? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and let’s continue the exploration together.
Explain Why Dna Replication Is Considered To Be Semi-Conservative
Image: pediaa.com
An article about Explain Why Dna Replication Is Considered To Be Semi-Conservative has been read by you. Thank you for visiting our website, and we hope this article is beneficial.